Rivers Of Hope CEO Francineglide Victoria Joins the Rotary Club Of Taunton
Taunton, MA – April 2024 Immediate Release For Immediate Distribution Rivers of Hope is pleased to announce that Francineglide Victoria,
Compassionate In-Home Care Services For Seniors And Individuals With Disabilities

Taunton, MA – April 2024 Immediate Release For Immediate Distribution Rivers of Hope is pleased to announce that Francineglide Victoria,

Winter brings both chilly weather and safety concerns for our cherished seniors. Creating a safe environment is crucial, considering challenges

Autism is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that affects communication, social interaction, and behavior. It is estimated that 1 in 36

FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Rivers of Hope Receives Home Care Agency Accreditation from the Home Care Alliance of Massachusetts, Inc. Brockton,

• The Medicare open enrollment period is specific to people who are already enrolled in Medicare, so if you are
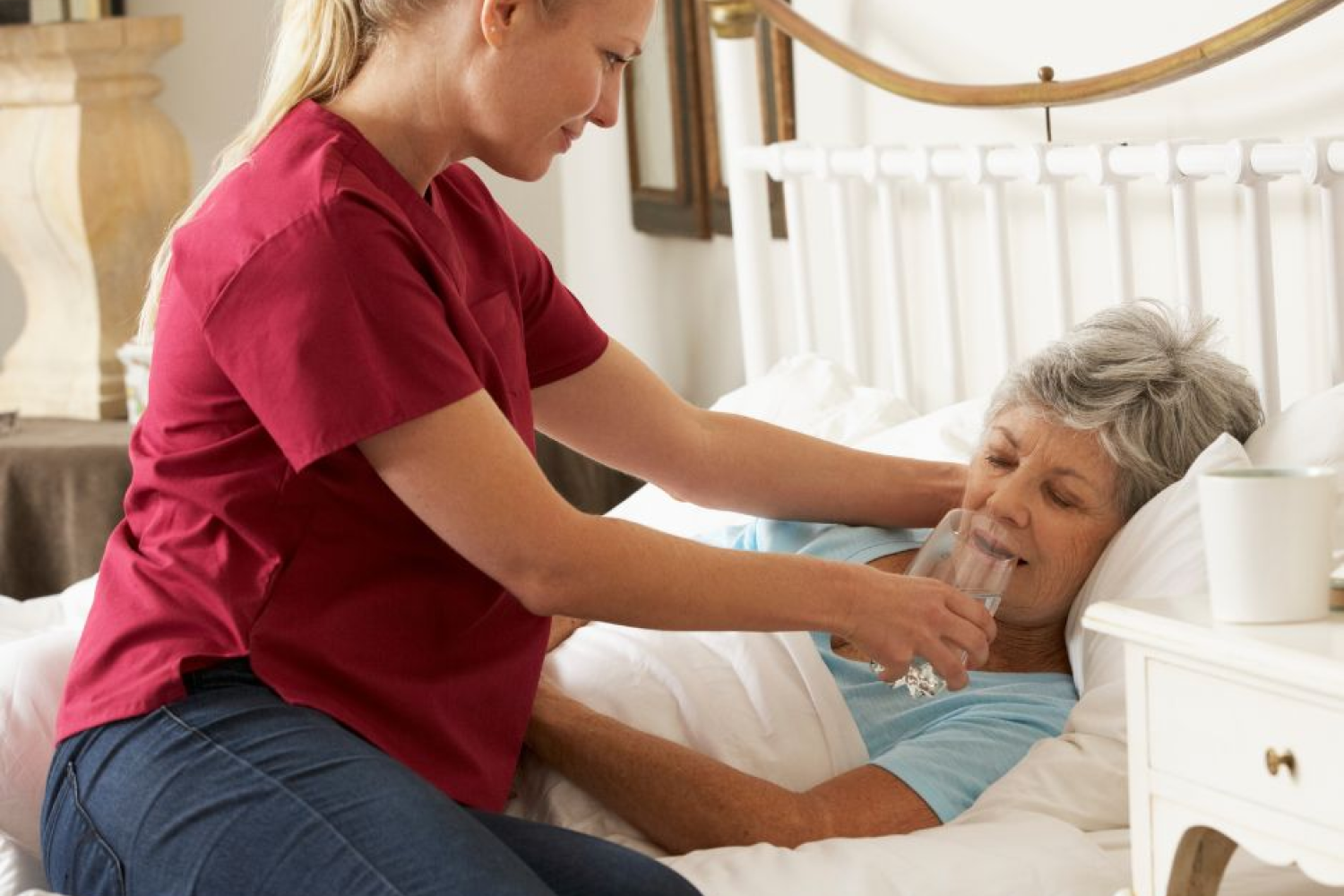

More benefits of drinking water than just quenching thirst. Given that our bodies contain roughly 60% water, maintaining hydration is

It’s already July, which means this 4th of July weekend will be filled with fun, family, and fireworks. But Independence

Father’s Day can be made even more enjoyable with senior-friendly activities. Spending quality time with the significant man (or men)

Dehydration is harmful to the health of seniors. Everyone, but especially older persons who are more susceptible to dehydration, should


RiversofHope received 3 years of accreditation.
Copyright © 2024 Rivers Of Hope. All rights reserved